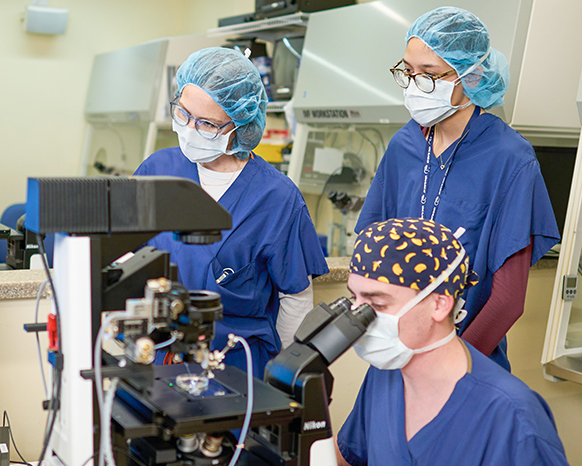
At RMA of New York – Long Island, our Preimplantation Genetic Testing Program, first introduced over a decade ago, combines our expert technology and IVF experience with access to advanced genetic testing and counseling. We recommend that those patients interested in pursuing PGT have a consultation with a genetics counselor prior to their IVF cycle.
How Preimplantation Genetic Testing Is Performed
PGT is performed in conjunction with IVF. In most cases, there are multiple embryos created and available for genetic analysis. The embryos are incubated for 5 to 6 days, which is when they reach the blastocyst stage of embryonic development. At this point, the embryo is a ball of rapidly-dividing cells and consists of an inner mass and an outer shell, known as the trophectoderm. In later stages of development, the inner mass becomes the fetus and the trophectoderm becomes the placenta.
During the blastocyst stage, a biopsy is performed and several cells are removed from the trophectoderm. This has no effect on the embryo’s ability to continue normal development. The biopsied sample is then analyzed in a specialized laboratory. While the testing is in progress, the embryos are cryopreserved (frozen). Once the results are received and a viable embryo has been identified, patients can begin a frozen embryo transfer cycle, which involves thawing the cryopreserved embryo and preparing the uterus for implantation.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Aneuploidy (PGT-A)
Preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A), formerly known as preimplantation genetic screening or PGS, is the process of evaluating embryos to ensure each one has 23 pairs of chromosomes. The average human being has a total of 46 chromosomes, inheriting half from their mother and half from their father. Together, these 23 chromosome pairs determine our characteristics, as well as our overall development. Because our bodies require exactly 46 chromosomes to function and develop properly, an extra or missing chromosome can disrupt normal development.
Aneuploidy refers to any condition characterized by an abnormal number of chromosomes. Many chromosomally abnormal embryos either do not implant, result in pregnancy loss (miscarriage) shortly after implantation, or result in a pregnancy with chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down Syndrome. PGT-A allows us to screen embryos and only use ones that have the ideal number of chromosomes for implantation, thus increasing the chance of achieving a healthy full-term pregnancy.
PGT-A is most commonly performed in the following situations:
- Advanced maternal age – chromosomal abnormalities are more likely to occur in women over the age of 35. PGT-A testing can determine the number of chromosomes and determine which embryos are the most likely to result in a healthy pregnancy.
- Recurrent miscarriages or repeated unexplained IVF embryo implantation failure – PGT-A testing can determine which embryos are the most likely to result in a healthy pregnancy.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Structural Chromosomal Rearrangements (PGT- SR)
While PGT-A is used to detect abnormal numbers of chromosomes, preimplantation genetic testing for structural chromosomal rearrangements (PGT-SR) is used to detect aberrant structural mutations of the chromosomes themselves. These mutations include:
- Duplication: when a segment of a chromosome has extra copies
- Deletion: when a segment of a chromosome is missing
- Inversion: when a segment of a chromosome breaks off and reattaches elsewhere on the same chromosome
- Translocation: when a segment of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to a different chromosome
PGT-SR is typically recommended for patients who are known carriers of existing chromosomal mutations.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic/Single Gene Defects (PGT-M)
PGT is also available for prospective parents who are concerned about the possibility of passing on genetic diseases to their children. Preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic/single gene defects (PGT-M), also known as preimplantation genetic diagnosis or PGD, is the process of genetically analyzing embryos for specific mutations carried by the parents (e.g. Cystic Fibrosis).

Why RMA of New York – Long Island: Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Since 1988, RMA of New York – Long Island has provided fertility patients throughout Nassau and Suffolk Counties with advanced, high-level fertility care, including comprehensive genetic testing. Our unique approach to infertility care is firmly rooted in creating an individualized experience for each patient, using the safest and most effective technologies available, all with the convenience of being a local, neighborhood practice. When you walk into one of our fertility clinics, you can expect to work with a compassionate team that is dedicated to guiding you along your family-building path.
Visit us at one of our six convenient locations on Long Island, or request a consultation and take the first step toward growing your family.
Get Started
It’s never too early to learn about your fertility and reproductive options.
Have questions? We can help.
Patient-centric reproductive medicine is our specialty, and we look forward to answering any questions you may have.








